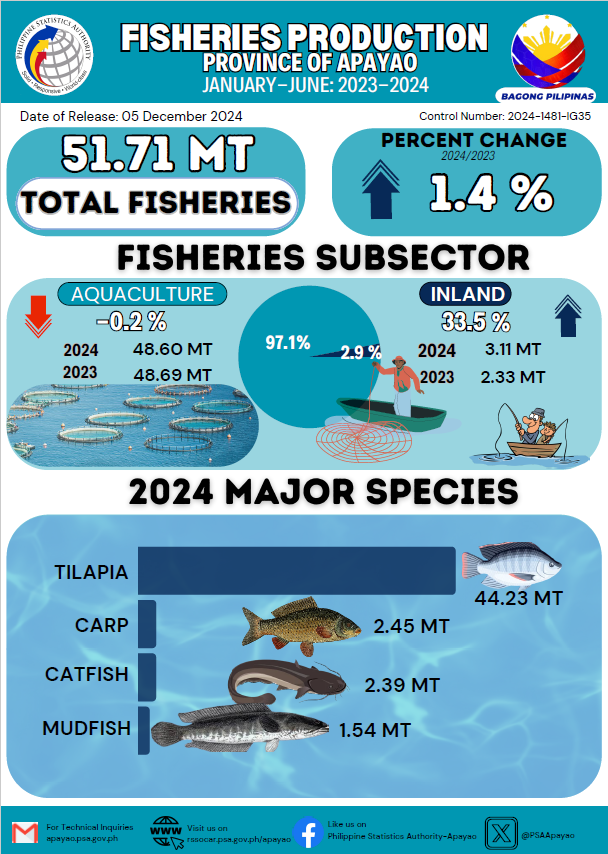
This special release presents the value of production in agriculture and fisheries in the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR), measured at constant 2018 prices. The valuation is disaggregated by sub-commodity group: crops, livestock, poultry, and fisheries. These data serve as inputs in estimating the Gross Value Added (GVA) of agriculture and fisheries at the regional level.
The regional value of production covers all agricultural commodities, with selected commodities highlighted in CAR. For crops, 22 commodities are featured. For fisheries, nine (9) commodities are covered. Meanwhile, all commodities included in the livestock and poultry data system are presented.
TOTAL AGRICULTURE AND FISHERIES
Figure 1. Value of Production of Agriculture & Fisheries, CAR: 2022-2024
(In Million Pesos, at Constant 2018 Prices)
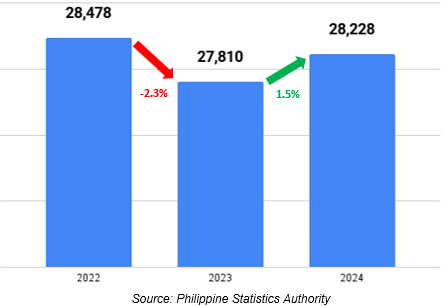
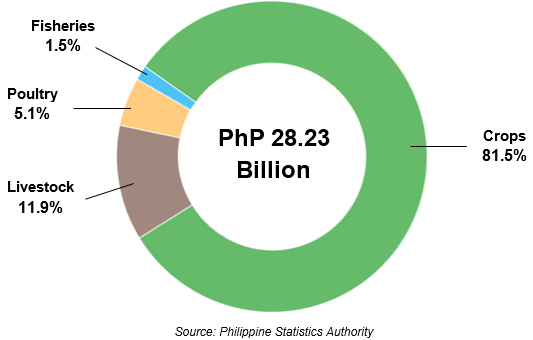
In 2024, the value of production in agriculture and fisheries in the Cordillera Administrative Region, at constant 2018 prices, amounted to PhP 28.23 billion. This reflected a 1.5% increase from PhP 27.81 billion in 2023 (Figure 1). The crops sub-sector accounted for the largest share of the total value, at 81.5%, followed by livestock and poultry with shares of 11.9% and 5.1%, respectively. Fisheries contributed the smallest share at 1.5% (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Percent Distribution by Sub-sector of Total
Value of Production, CAR: 2024
CROPS
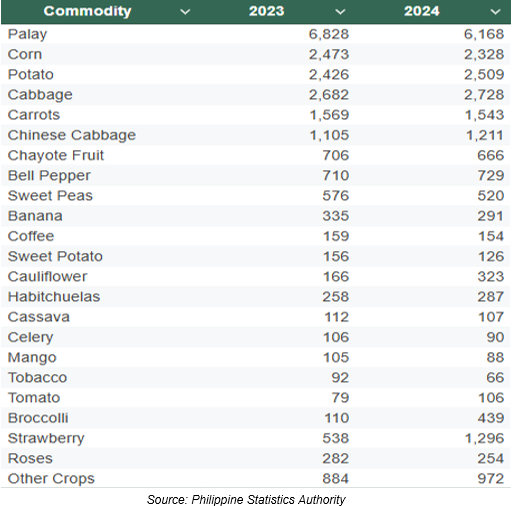
The total value of crops production at constant 2018 prices was recorded at PhP 23.00 billion in 2024, 2.4% higher than the 2023 level of PhP 22.45 billion (Figure 3). The top six crops with the highest value of production were palay, cabbage, potato, corn, carrots, and strawberry, with corresponding values of PhP 6.17 billion, PhP 2.73 billion, PhP 2.51 billion, PhP 2.33 billion, PhP 1.54 billion, and PhP 1.30 billion, respectively (Table 1).
Figure 3. Value of Production of Crops, CAR: 2023-2024
(In Billion Pesos, at Constant 2018 Prices)
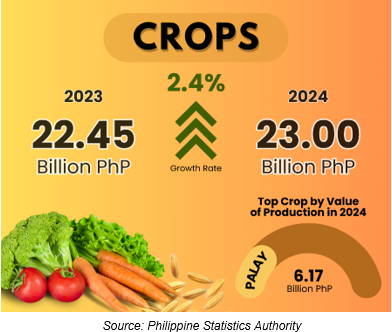
Table 1. Value of Production of Crops by Commodity, CAR: 2023-2024
(In Million Pesos, at Constant 2018 Prices)
LIVESTOCK
Figure 4. Value of Production of Livestock, CAR: 2023-2024
(In Billion Pesos, at Constant 2018 Prices)
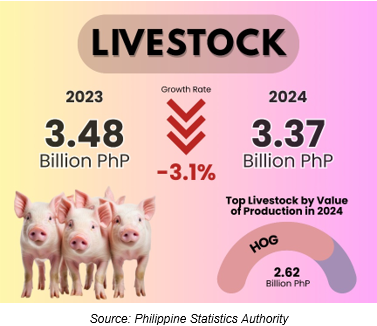
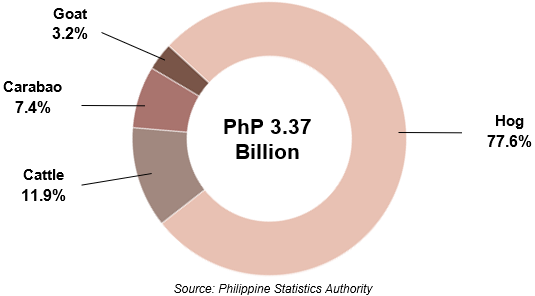
At constant 2018 prices, the total value of livestock production in the Cordillera Administrative Region was estimated at PhP 3.37 billion in 2024, representing a 3.1% decline from the 2023 level of PhP 3.48 billion (Figure 4). Swine remained the top contributor with a 77.6% share, followed by cattle with 11.9%, carabao with 7.4%, and goat with 3.2% (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Percent Distribution by Commodity of the Total
Value of Livestock Production, CAR, 2024
POULTRY
Figure 6. Value of Production of Poultry, CAR: 2023-2024
(In Billion Pesos, at Constant 2018 Prices)
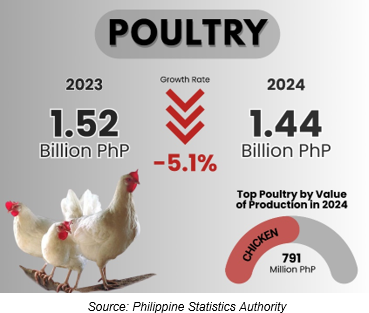
At constant 2018 prices, the total value of poultry production in 2024 was estimated at PhP 1.44 billion. Chicken had the highest contribution to the total, accounting for 54.8%, followed by chicken eggs with 34.4%. Duck and duck eggs contributed 6.5% and 4.2%, respectively (Figure 8).
Figure 7. Percent Distribution by Commodity of the Total
Value of Poultry Production, CAR: 2024
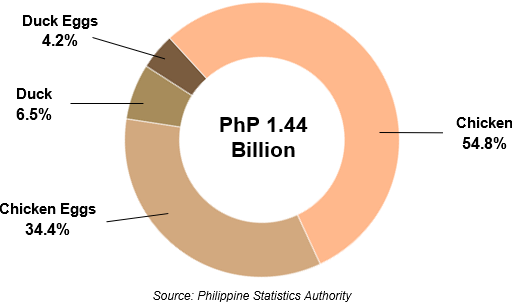
Figure 8. Value of Production of Fisheries, CAR: 2023-2024
(In Million Pesos, at Constant 2018 Prices)
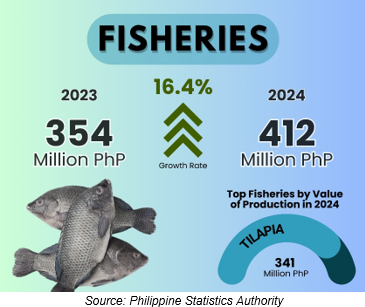
Fisheries contributed 1.5% to the total value of production in agriculture and fisheries, posting a 16.4% increase, from PhP 354 million in 2023 to PhP 412 million in 2024. Tilapia had the largest share among species, accounting for Php 341 million, or 82.8% of the total (Table 2).
Table 2. Value of Production of Fisheries by Commodity, CAR: 2023-2024
(In Million Pesos, at Constant 2018 Prices)

(SGD)
ALDRIN FEDERICO R. BAHIT, JR.
(Chief Statistical Specialist)
Officer-In-Charge
/AFRBJ/KAMC/NAGD
Technical Notes
Value of Production at Constant Prices - refers to the valuation of transactions wherein the influence of price changes from the base year to the current year has been removed.
Crops Production - refers to the quantity produced and harvested for a particular crop during the reference period. It includes those measured but damaged, stolen, given away, consumed, given as harvesters’ share, and reserved. Also included are those productions from “pakyaw” and “contract growers”. On the other hand, excluded are those produced but not harvested for whatever reason/s.
Livestock/Poultry Production -refers to the volume of indigenous (locally-raised) animals disposed of for slaughter, plus animals exported or shipped-out for slaughter, both in liveweight equivalent.
Livestock - refers to farm animals kept or raised for consumption, work, or leisure. In general, poultry is separated as a distinct group of farm animals. For purposes of censuses and surveys, livestock covers only those that are tended and raised by an operator.
Poultry- a collective term for all domesticated avian for food consumption, or the carcass of such avian is processed for human consumption.
Swine – a non-ruminant, cloven-footed animal belonging to the family Suidae with a simple stomach, having a snout, a large number of mammary glands, thin skin, and heavy bristles. It is also called a hog or a pig.