CAR literacy rate is at 96.1%
Based on the 2020 Census of Population and Housing (2020 CPH), of the 1,632,709 household population five years old and over in the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR), 1,568,486 persons (96.1%) were literate.
In the 2020 CPH and 2015 Census of Population (2015 POPCEN), a person is considered literate if he/she is able to read and write a simple message in any language or dialect.
Literacy rate in 2020 in CAR was slightly higher among males with 96.1% than among females with 96.0% (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Literacy Rate Among Household Population Five Years Old and
Over by Sex, CAR: 2020

More males are literate than females
There were more literate males than females from ages 5-59 years. The number of literate males was highest among ages 15-19 years with a household population of 90,066 for males compared to 87,087 of females (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Literacy of Household Population Five Years Old and Over by Age Group
and Sex, CAR: 2020

Figure 3. Literacy Rate of Household Population Five Years Old and
Over by Age Group and Sex, CAR: 2020
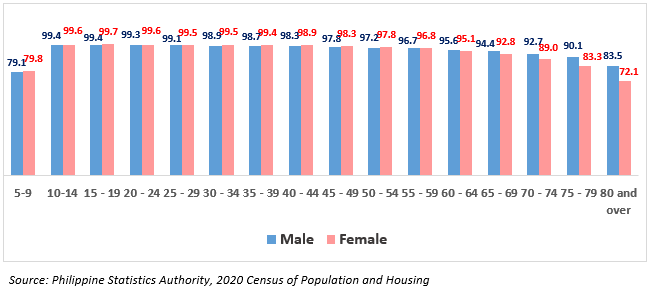
In general, literacy rate across all age groups from 5 years and over was high in 2020. It was highest at more than 99.0% among ages 10-39 years (Figure 3).
Figure 4. Literacy Rate of Household Population Five Years Old and Over
by Region, Philippines: 2020

The National Capital Region (NCR) posted the highest literacy rate among 17 regions with 98.9%. Other regions that posted a literacy rate higher than the national rate (97.0%) were Region I – Ilocos Region (98.6%), Region IV-A CALABARZON (98.5%), Region III – Central Luzon (98.3%), Region II – Cagayan Valley (98.0%), Region VI – Western Visayas (97.7%), Region V – Bicol Region (97.4%), and Region VII – Central Visayas (97.1%).
CAR recorded a 96.1% literacy rate of persons 5 yrs old and over in 2020. The region ranked 11th among the 17 regions.
Meanwhile, the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) had the lowest literacy rate with 86.4%.
One in three of the household population reaches or completes high school or secondary level
In the 2020 Census of Population and Housing, the highest educational attainment was asked for all persons aged five years and over. The census revealed that 34.3% of the 1,632,709 household population of 5 years old and over in CAR had reached or completed at most high school or secondary level (Figure 5). There were about 18.0% graduates, while 16.2% were undergraduates. On the other hand, 27.4% (447,261) had reached or completed at most elementary level with 9.5% graduates and 20.0% undergraduates (Figure 5). About 28.6% (466,243) had reached or completed at most college level with 8.7% graduates and 18.6% undergraduates (Figure 5).
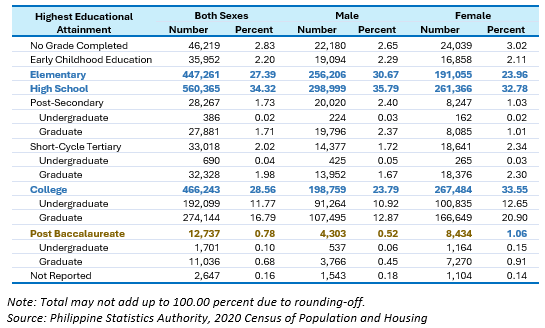
Meanwhile, 0.8% had reached or completed Post-Baccalaureate level. Further, more females attain higher levels of education than males with 1.06% compared to 0.78% of males (Figure 6).
Figure 5. Proportion of Household Population Five Years Old and Over by Highest Educational Attainment, CAR: 2020

Figure 6. Household Population Five Years Old and Over by Highest Educational Attainment and Sex, CAR: 2020
About 7 in every 10 children aged 5-9 years old (67.1%) had reached or completed elementary education.
All children (114,709) aged 5-9 years old had reached or completed at most elementary education under the K to 12 Curriculum, 20.6% had reached or completed at most Early Childhood Education. Meanwhile, and 11.9% had no grade completed.
On the other hand, 56.7% (99,564) of the 175,745 children aged 10-14 years had reached or completed at most elementary education under the K to 12 Curriculum, while 42.5% (74,670) had reached Junior High School (JHS) which is composed of Grades 7 to 10 under the new K to 12 Curriculum.
Moreover, 46.9% (83,653) of the 178,302 household population aged 15-19 years had reached or completed at least JHS, while 31.5% (56,135) reached or completed at most SHS.
Of the household population (174,000) aged 20-24 years, 57.6% (100,188) had reached or completed at most college education.
(SGD)
VILLAFE P. ALIBUYOG
Regional Director
Technical Notes
Household is a social unit consisting of a person or a group of persons who sleep in the same housing unit and have a common arrangement in the preparation and consumption of food.
Household population refers to all persons who are members of the household.
Sex is the biological and physiological reality of being a male or female.
Age refers to interval of time between the person’s date of birth and his/her last birthday prior to the census reference date. It is expressed in completed years or whole number.
Simple literacy is the ability of a person to read and write a simple message. As such, a person is said to be literate if he/she can both read and write a simple message in any language or dialect. A person who cannot read and write a simple message, such as “I CAN READ” is considered illiterate. Moreover, a person is still considered illiterate if he/she is capable of reading and writing only his/her own name or numbers. Similarly, a person is illiterate if he/she can read but not write or he/she can write but not read.
A person who knows how to read and write but at the time of the census can no longer read and/or write due to some physical defect or illness is still considered literate. Example of this is an aged person who knows how to read and write but can no longer perform these activities due to poor eyesight or hand injury. Persons with disability who can read and write through other means such as the use of Braille are considered literate.
Highest grade/year completed refers to the highest grade or year completed in school, college, or university as of 01 May 2020. This may be any one of the specific grades or years in elementary, high school, K to 12 Program, and college. It may also be special needs education program, second-chance education program, or any of the post-secondary, short-cycle tertiary, college, and post baccalaureate courses.
In 2011, the Department of Education (DepEd) implemented the K to 12 Program. Under this program, the education of a person starts in Kindergarten, followed by an Elementary education of six years from Grade 1 to Grade 6, Junior High School education of four years from Grade 7 to Grade 10, and Senior High School education of two years from Grade 11 to Grade 12.
Old Curriculum covers preschool, six to seven years in elementary from Grade 1 to Grade 6 or Grade 7, and four years in high school from 1st year to 4th year.
Inclusive/Special Needs Education (SPED) Program is designed to facilitate learning by individuals who, for a wide variety of reasons, require additional support and adaptive pedagogical methods in order to participate and meet learning objectives in an education program. Reasons may include (but are not limited to) disadvantages in physical, behavioral, intellectual, emotional and social capacities. For purposes of the 2020 CPH, this includes gifted or talented individuals.
- Special Needs Education Program in Primary Level (elementary) includes programs suited to individuals with special needs that are designed to provide systematic teaching and learning in the fundamental skills of reading, writing, and mathematics, irrespective of the age of the participant.
- Special Needs Education Program in Secondary Level (high school) includes programs suited to individuals with special needs that are designed to build on the fundamental teaching and learning processes that begin at elementary level and/or provide skills relevant to employment.
Second-Chance Education Programs in Primary Level refers to the program that usually targets individuals who: (1) left school before completing primary education, allowing them to re-enter the education system and complete primary education or (2) completed primary education but wish to enter an education program or occupation for which they are not yet qualified.
Second-Chance Education Programs in Secondary Level refers to the program that usually targets individuals who: (1) left education after completing primary education but before completing lower secondary education, allowing them to re-enter the education system and complete a lower secondary education program or (2) completed lower secondary education but wish to enter an education program or occupation for which they are not yet qualified.
Postsecondary or Post-secondary Non-tertiary Education provides learning experiences building on secondary education, preparing graduates for labor market entry as well as tertiary education. Programs are not considered to be tertiary education and are typically vocational and terminal programs that prepare graduates for the labor market.
Short-cycle Tertiary Education captures the lowest level of tertiary education and also includes advanced technical and vocational education and training (TVET). Programs at this level have more complex contents than programs in senior high school and post-secondary non-tertiary education, but are shorter and less theoretically-oriented than a Bachelor's program. Although they are usually designed to prepare for employment, they may give credit for transfer into a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree.
Bachelor-Level Education is designed to provide participants with intermediate academic and/or professional knowledge, skills and competencies, leading to a first degree equivalent qualification. It typically has duration of three to four years of full-time study at the tertiary level. Traditionally offered by universities and equivalent tertiary educational institutions, it does not necessarily require the preparation of a substantive thesis or dissertation.
Post Baccalaureate course refers to any course for which an undergraduate degree or bachelor’s degree is required.
Master-Level Education is designed to provide participants with advanced academic and/or professional knowledge, skills and competencies, leading to a second degree or equivalent qualification and has a substantial research component but do not yet lead to the award of a doctoral qualification.
Doctoral-Level Education is designed primarily to lead to an advanced research qualification and devoted to advanced study and original research. Typically offered by research-oriented tertiary educational institutions such as universities, doctoral programs exist in both academic and professional fields. The theoretical duration of this program is three years full-time in most countries, although the actual time that students take to complete the program is typically longer.


