Table A. Year-on-Year Inflation Rates, All Items
In percent
(2018=100)
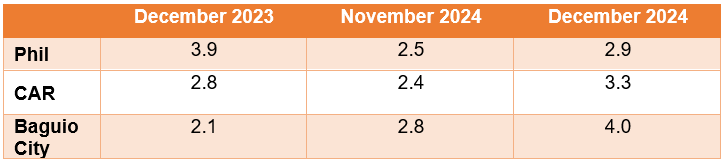
Figure 1. Headline Inflation Rates in Baguio City, All Items
(2018=100)
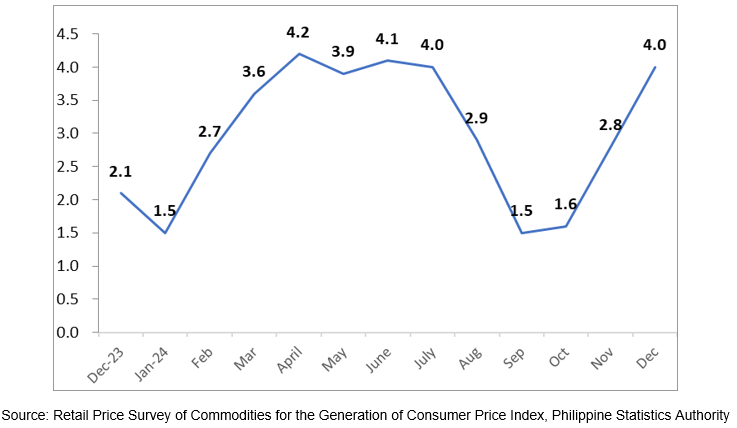
Table B. Year-on-Year Inflation in Baguio City, By Commodity Groups
In percent
(2018=100)
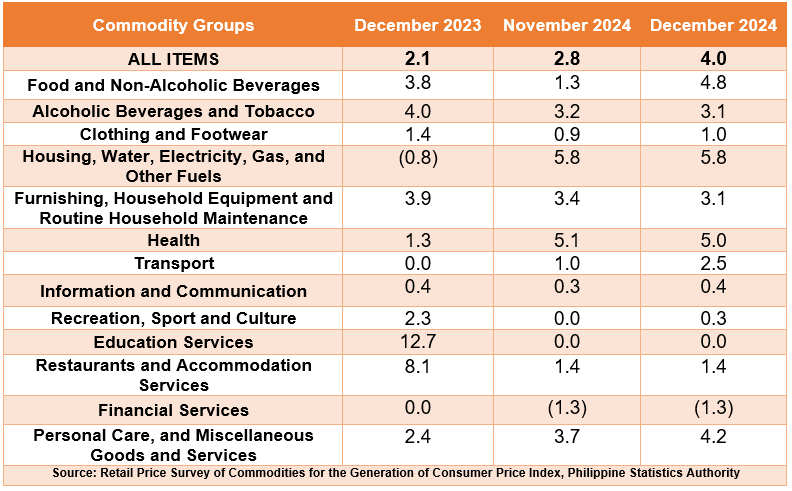
Table C. Year-on-Year Food Inflation in Baguio City
In percent
(2018=100)
Baguio City
Headline Inflation
The headline inflation or overall inflation of the city increased to 4.0 percent in December 2024 from 2.8 percent in November 2024. In December 2023, the inflation rate was 2.1 percent. (Figure 1, and Tables A and B)
Main Drivers to the Upward Trend of the Headline Inflation
The uptrend in the overall inflation in December 2024 was primarily brought about by the higher annual increment of food and non-alcoholic beverages at 4.8 percent from 1.3 percent in the previous month. Also contributing to the uptrend was transport with 2.5 percent from 1.0 percent, and personal care, and miscellaneous goods and services with 4.2 percent from 3.7 percent.
Higher annual increment were also noted in the index of the following:
a. Clothing and footwear, 1.0 percent from 0.9 percent;
b. Information and communication. 0.4 percent from 0.3 percent; and
c. Recreation, sport and culture, 0.3 percent from 0 percent.
On the contrary, the index of the following exhibited a slower annual increase during the month:
a. Alcoholic beverages and tobacco Clothing and footwear, 3.1 percent from 3.2 percent;
b. Furnishings, household equipment and routine household maintenance, 3.1 percent from 3.4 percent;
c. Health, 5.0 percent from 5.1 percent.
The indices of the rest of the commodity groups retained their respective previous month’s annual rates.
Main Contributors to the Headline Inflation
The top three commodity groups contributing to the October 2024 overall inflation were the following:
a. Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels;
b. Food and non-alcoholic beverages; and
c. Transport.
Food Inflation
Food inflation at the provincial level increased to 4.8 percent from 1.1 percent in the previous month. In December 2023, food inflation was higher at 3.9 percent. (Table C)
Main Drivers to the Upward Trend of Food Inflation
The acceleration of food inflation in December 2024 was primarily brought about by vegetables, tubers, plantains, cooking bananas and pulses with 6.0 percent from -10.5 percent. This was followed by fruits and nuts with 11.1 percent from 4.9 percent, and fish and other seafood with -0.8 percent from -3.5 percent.
Moreover, higher inflation rate during the month were also noted on the following:
a. Cereals and cereal products, 6.9 percent from 6.6 percent;
b. Meat and other parts of slaughtered animals, 5.5 percent from 4.4 percent;
c. Oils and fats, 2.9 percent from 1.5 percent; and
d. Sugar, confectionery and desserts, 1.4 percent from 0.8 percent.
In contrast, ready-made food and other food products decreased from 4.4 percent to 4.0 percent.
Main Contributors to the Food Inflation
The top three food groups in terms of contribution to the food inflation during the month were the following:
a. Cereals and cereal products;
b. Meat and other parts of slaughtered land animals; and
c. Fruits and nuts.
Note: CPIs and inflation rates by region, province and selected city are posted at the PSA website (https://openstat.psa.gov.ph/).
IMELDA L. BUYUCCAN (SGD)
Chief Statistical Specialist
/SMBP

