Data on health indicators presented in this special release were obtained from the results of the Key Indicators Report of the 2022 National Demographic and Health Survey (NDHS). The 2022 NDHS is the seventh Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) conducted in the Philippines in collaboration with the worldwide DHS program, and the 12th in a series of NDHS conducted every five years since 1968.
The 2022 NDHS provides information on the basic demographic and health indicators, specifically on fertility, fertility preferences, family planning practice, childhood mortality, maternal and child health, nutrition, knowledge and attitudes, regarding HIV/AIDS, violence against women, child discipline, early childhood development and other health issues. These indicators are crucial in policymaking, program planning, and monitoring and evaluation of population and health programs, including those related to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
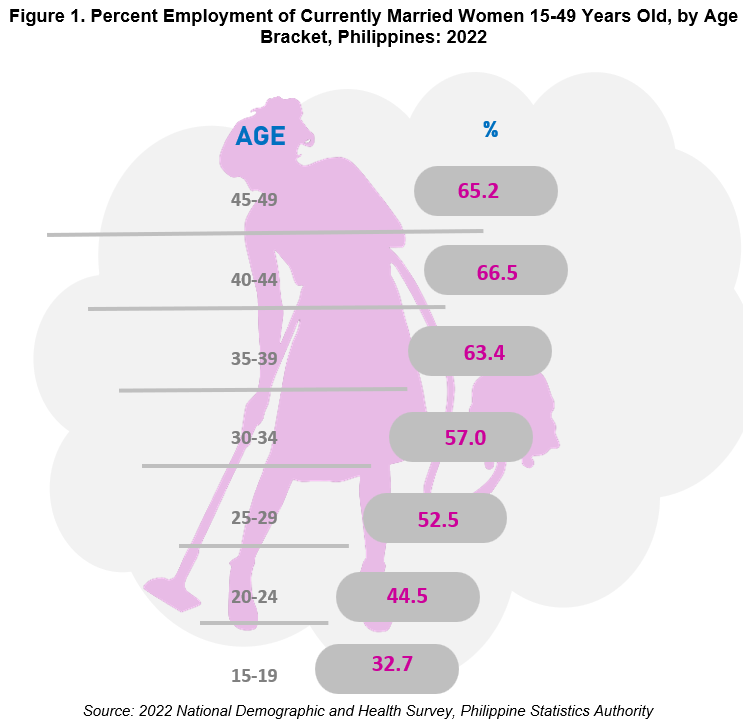
6 in 10 currently married women in the Philippines are employed.
In 2022, 59.2 percent of the population of currently married women aged 15-49 years old were employed within 12 months preceding the survey. This increased by one person employed compared to the employment of married women in 2017 with 58.2 percent.
In general, employment among currently married women increased with age wherein those belonging to the age group 40-44 had the highest employment with 66.5 percent, followed by the age group 45-49 with 65.6 percent, and age 35-39 with 63.4 percent.
Employment of currently married women belonging to the age group 30-34 had 57.0 percent employment, age group 25-29 with 52.5 percent, age group 20-24 with 44.5 percent, and age group 15-19 with 32.7 percent.
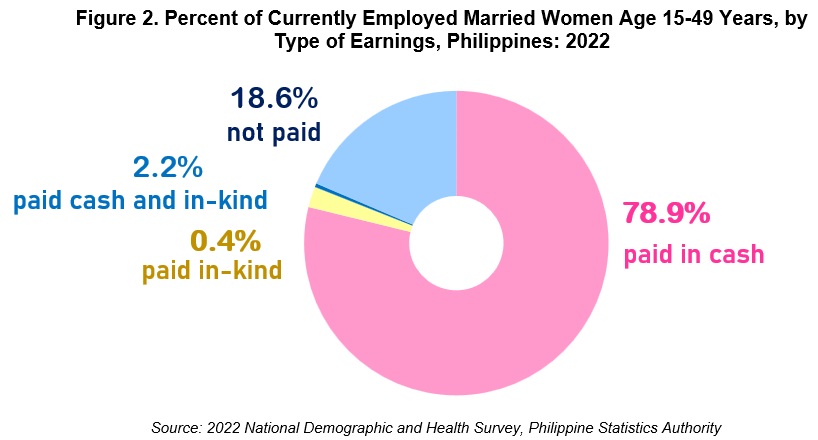
Of the employed married women, 78.9 percent were paid in cash, while 18.6 percent were not paid for their work. About 2.2 percent were paid in cash and in-kind, while those paid in-kind only were about 0.4 percent.
Both husband and wife decide on how to spend the wife’s cash earnings.
In 2022, 55.5 percent of currently married women aged 15-49 years in the country claim that both husband and wife had control over the wife’s cash earnings. On the other hand, 39.8 percent decided on their own, while 4.7 percent said that their cash earnings were controlled by their husband.
At the regional level, the percentage of wives who claim that both husband and wife make decisions on how their cash earnings were spent was higher than at the national level. These regions include the following regions: MIMAROPA (69.0 percent), Region II-Cagayan Valley (67.8 percent), IX - Zamboanga Peninsula (64.9 percent), Region IVA-Calabarzon (64.0 percent), Region III-Central Luzon (59.8 percent), Region I-Ilocos (59.7 percent), Region XII – SOCCSKSARGEN (59.6 percent), and NCR (59.2 percent).
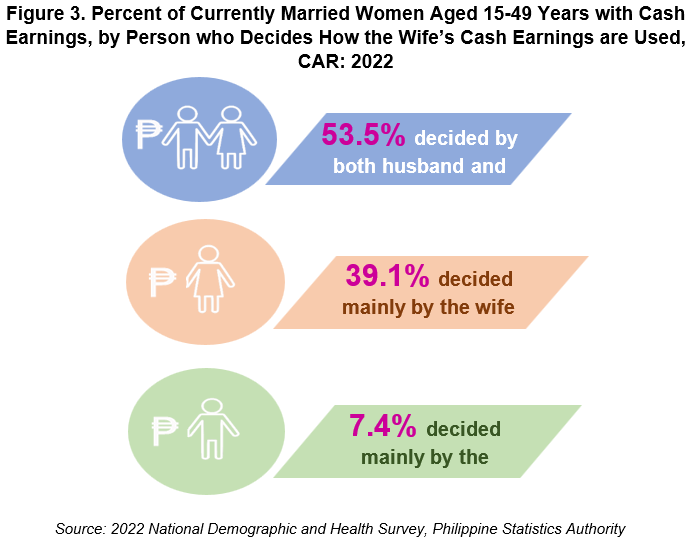
Meanwhile in CAR, more than half (53.5 percent) of currently married women aged 15-49 years said that the decision on how the wife’s cash earnings were spent was decided jointly by both the husband and the wife (Figure 3).
At the national level, the percentage of married women who had sole control over their earnings was about 39.8 percent.
In contrast to the findings at the national level, some regions had the most women who mainly decided about how their earnings were spent in 2022. These were Region IX-Davao (56.8 percent), Region VII-Central Visayas (55.4 percent), Region X-Northern Mindanao (53.6 percent), and Region XIII-Caraga (51.6 percent).
3 in 10 currently married women in CAR earn more than their husbands.
At the national level, the majority of currently married women who received compensation in cash, earn less than their husbands (45.0 percent). On the other hand, 26.2 percent of women earn more than their husbands, while 24.4 percent had cash earnings about the same amount as their husbands.
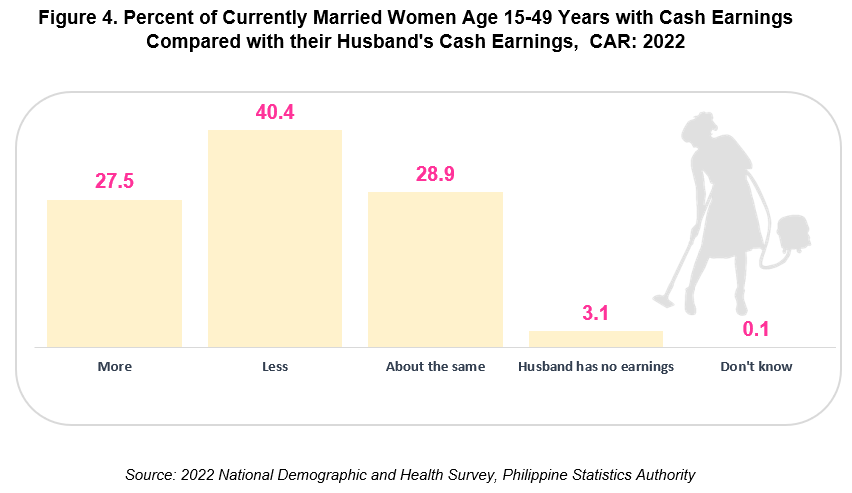
In CAR, currently married and employed women who earn more than their husbands was about 27.5 percent in 2022, while 40.4 percent earned less than their husbands, and 28.9 percent earned almost the same amount as their husbands (Figure 4).
Meanwhile, 3.1 percent of women were sole breadwinners or their husbands had no earnings at all.
The same trend of decision-making was reflected as that of the national level in the urban (54.2 percent) and rural (57.1 percent) areas wherein more wives claim that there is a shared decision between the husband and the wife on how the wife’s earnings were spent.
There is also not much difference in the situation at the national level in terms of decision-making over the wife’s earnings across the wealth quintile (55.5 percent).
More currently married women (48.3 percent) in rural areas reported less earnings than their husbands compared to wives in urban areas (42.6 percent).
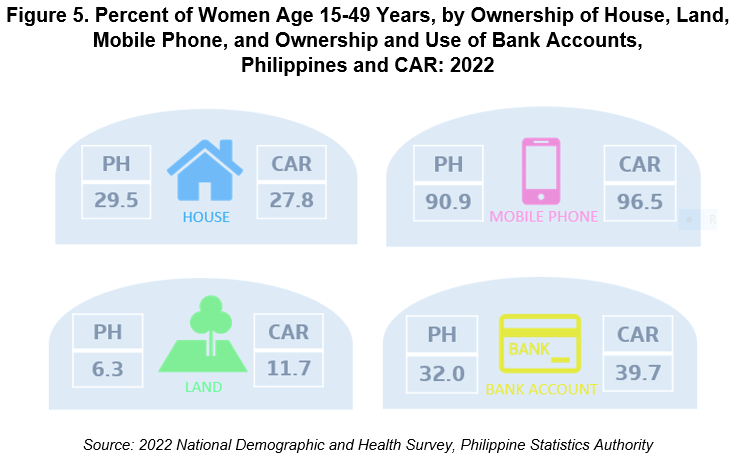
3 in 10 women own a house either solely, jointly or both.
In 2022, 29.5 percent of women age 15-49 years old own a house in any type of house ownership in the country. About 23.9 percent own the house jointly with someone else, while 5.3 percent own them solely and 0.3 percent have either both types of house ownership. On the other hand, a majority of women (70.5 percent) have yet to own a house.
In the Cordillera region, 72.2 percent of women do not own a house. About 23.7 percent of them own a house jointly with other people, while 4.0 percent of women had sole ownership of their houses.
Of those who own a house in any other form of ownership, 26.6 percent of women’s names appear on the title or deed, while 14.6 percent do not have their names on it. Meanwhile, 57.8 percent do not have any title/deed of their houses.
9 in 10 women do not own a land.
In 2022, majority of women (93.6 percent) do not own a land in the country. Of those who own a land (6.4 percent), joint ownership of the land accounted for 4.8 percent, while sole ownership recorded 1.4 percent.
Of the lands with titles/deeds, 27.1 percent of women’s names were on the title, while 18.5 percent do not have their names on the land titles/deeds.
Ownership of land by women in the rural areas is higher (8.9 percent) than in the urban areas (4.5 percent).
In CAR, a large group of women do not own a land (88.3 percent), while 11.7 percent of women own a land either solely, jointly, or both solely and jointly with someone else.
Regardless of land ownership, 28.9 percent had their names on the land tiles/deeds, while 16.7 percent do not have names on the titles/deeds.
9 in 10 women own a mobile phone, 3 in 10 women have and use a bank account.
In 2022, 90.0 percent of Filipino women own any type of mobile phone, with 84.7 percent owning a smartphone. Of those with mobile phones, almost half of them (48.6 percent) reported using them for financial transactions. About 32.0 percent of Filipino women had bank accounts and used mobile phones for depositing and withdrawing money.
The Cordillera region had a higher percentage of women owning a mobile phone with 96.5 percent wherein 91.4 percent of women reported using a smartphone. Meanwhile, about 56.6 percent of those who have bank accounts use their mobile phones for their financial transactions.
(SGD)
VILLAFE P. ALIBUYOG
Regional Director
____________________________________
TECHNICAL NOTES
Employment - Respondents are considered to be employed if they have done any work other than their housework in the 12 months before the survey.
Earning cash for employment - Respondents are asked if they are paid for their labor in cash or in-kind. Only
those who receive payment in cash only or in cash and in-kind are considered to earn cash for their employment.
Control over one’s own cash earnings - Respondents are considered to have control over their own earnings if they participate in decisions alone or jointly with their spouse about how their own earnings will be used.
Ownership of a house or land Respondents who own a house or land, whether alone or jointly with their spouse, someone else, or both their spouse and someone else.
Documentation of ownership of a house or land - Respondents whose name is on the title/deed or other government-recognized document.
Use of bank accounts or mobile-money-service providers - Respondents who have and use a bank account or who used a mobile phone for financial transactions in the 12 months before the survey.


