Data on women empowerment and violence against women presented in this special release were obtained from the results of the Key Indicators Report of the 2022 National Demographic and Health Survey (NDHS). The 2022 NDHS is the seventh Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) conducted in the Philippines in collaboration with the worldwide DHS program, and the 12th in a series of NDHS conducted every five years since 1968.
The 2022 NDHS provides information on the basic demographic and health indicators, specifically on fertility, fertility preferences, family planning practice, childhood mortality, maternal and child health, nutrition, knowledge and attitudes, regarding HIV/AIDS, violence against women, child discipline, early childhood development and other health issues. These indicators are crucial in policymaking, program planning, and monitoring and evaluation of population and health programs, including those related to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
About 3 in 10 of the married women in CAR makes more money than their husband or partner
Among the married women in CAR who receive cash earnings, 27.5% claim to earn more than their husband or partner, while a higher proportion (28.9%) earn roughly the same amount. Meanwhile, 2 in 5 of these women earn less than their husband.
Furthermore, among married women aged 15-49 who received cash earnings from employment in the 12 months preceding the survey, 7.4% had their husband or partner primarily deciding on the use of women's earnings, while 53.5% made decisions jointly with their husband or partner. The remaining 39.1% of these women primarily made decisions on their earnings themselves.
Figure 1. Percentage of Currently Married Women 15-49 Years Old
by Participation in Decision Making, CAR: 2022
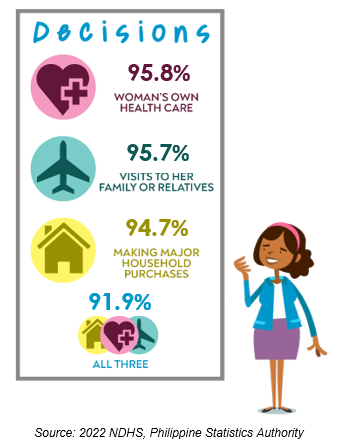
Married women are most involved in making decisions about own health care
Among regions, CAR had the highest percentage of married women aged 15 to 49 who were involved in all three specified decisions, either independently or in conjunction with their husbands, at 91.9%.
In 2022, 96% of currently married women aged 15-49 in CAR had input on decisions related to their own healthcare. Additionally, majority of married women in CAR were involved in other specific decisions, including visits to the wife's family or relatives (95.7%), and making major household purchases (94.7%).
About 9 in 10 wives in CAR participated in making decisions regarding the specific matters mentioned above, while 2.3% of married women said that they were not involved in making any of the three specific decisions.
Figure 2. Percentage of Women 15-49 Years Old who Agree that a Husband
is Justified in Hitting or Beating his Wife for Specific Reasons, CAR: 2022
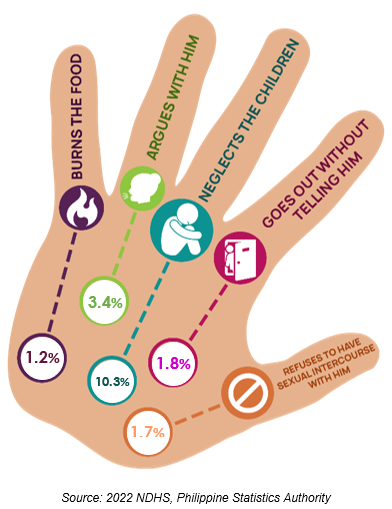
Some women say wife beating is justifiable under certain instances
In 2022, a minority of women agreed that the husband is justified in hitting or beating his wife if she: neglects the children (10.3%); argues with him (3.4%); goes out without telling him (1.8%); refuses to have sexual intercourse with him (1.7%); and burns the food (1.2%). Further, 1 in 10 Cordilleran woman concurred with at least one of the specified reasons above. About 13.0% of the Cordilleran women agree with at least one of the specified reasons in justifying the husband in beating his wife.
Generally, attitudes rationalizing wife beating exhibit an indirect relationship with educational attainment. This means that as women achieve higher levels of education, they tend to invalidate reasons justifying physical domestic violence against women. The same relationship was observed between attitudes justifying wife beating and household wealth.
Figure 3. Percentage of Women 15-49 Years Old who have ever
Experienced Violence Committed by their Current or Most Recent
Husband/Intimate Partner, CAR: 2022

Violence has been experienced by 1 out of 5 women in CAR who have been in a marital or intimate relationship
Approximately 20% of women in CAR who have been in a relationship with a husband or intimate partner had encountered some form of violence from their most recent partner. Emotional violence was experienced by 18.0% of Cordilleran women, 5.1% experienced physical violence, and 2.7% experienced sexual violence.
When the husband or intimate partner is not already beating or physically hurting the wife or partner, a counter violence might be committed by the woman against the former. About 7.2% of women in the country who have been in a relationship with a husband or intimate partner have ever perpetrated physical violence against their current or most recent partner. Incidence was lower in CAR with 3.5%.
Figure 4. Percentage of Women 15-49 Years Old who ever Experienced
Physical or Sexual violence by their Help-seeking Behavior, CAR: 2022

About 2 in 5 women in CAR who have encountered violence refrained from seeking assistance
When it comes to addressing various forms of violence, 46.0% of women in CAR who endured physical or sexual violence sought assistance, while 16.0% shared their experiences with someone but did not seek help. The remaining 38.0% neither sought assistance nor shared their experience with anyone.
About 9 in 10 women in CAR knew that they can seek assistance from PNP Women and Children’s Protection Desk, Barangay VAW Desk and DSWD Regional Center for Women or Girls. In addition, about 7 in 10 women were aware that they can seek help also from PAO-DOJ or any legal assistance office, Women and Children’s Protection Unit, and Temporary or Permanent Protection Desk per RA 9262. More than half of these women also knew that they can ask the help from CSOs, NGOs and people’s organization.
(SGD)
VILLAFE P. ALIBUYOG
Regional Director
AFRB/RJPA/JRFB
--TECHNICAL NOTES--
Employment
Respondents are considered to be employed if they have done any work other than their housework in the 12 months before the survey.
Earning cash for employment
Respondents are asked if they are paid for their labor in cash or in-kind. Only those who receive payment in cash only or in cash and in-kind are considered to earn cash for their employment.
Control over one’s own cash earnings
Respondents are considered to have control over their own earnings if they participate in decisions alone or jointly with their spouse about how their own earnings will be used.
Participation in major household decisions
Women are considered to participate in household decisions if they make decisions alone or jointly with their husband in all three of the following areas: (1) their own health care; (2) major household purchases; and (3) visits to their family or relatives.
Attitudes toward wife beating
Respondents are asked if they agree that a husband is justified in hitting or beating his wife under each of the following five circumstances: she burns the food, she argues with him, she goes out without telling him, she neglects the children, and she refuses to have sex with him. If respondents answer “yes” in at least one circumstance, they are considered to have attitudes justifying wife beating.
Husband/intimate partner
The current husband for currently married women; the most recent husband for divorced, separated, or widowed women; the current intimate partner for never-married women who currently have an intimate partner; and the most recent intimate partner for never-married women who do not currently have an intimate partner but had one in the past.

