The Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) releases the country’s official poverty statistics for the basic sectors. PSA provides the estimates of poverty incidence for 10 of the 14 basic sectors identified in Republic Act 8425 or the Social Reform and Poverty Alleviation Act using the income and sectoral data from the merged Family Income and Expenditure Survey (FIES) and Labor Force Survey (LFS).
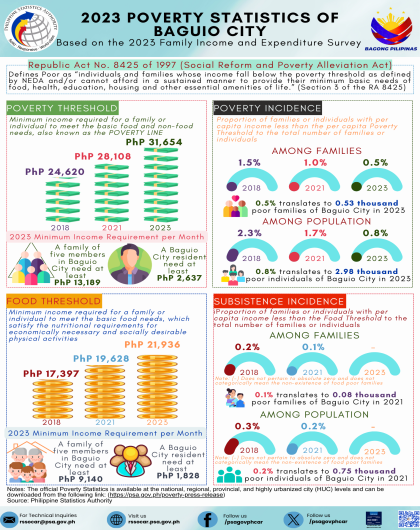
Farmers post highest poverty incidence in CAR in 2021
Farmers had the highest poverty incidence in CAR with 15.6 percent in 2021. This was followed by Children with 13.7 percent, and Rural residents with 13.5 percent. This means that these sectors had the highest proportion of individuals belonging to families with income below the official poverty thresholds compared to the other basic sectors of the population.

These three sectors also registered the highest poverty incidences in 2015 and 2018, except for rural residents where this sector ranked 4 with the highest poverty incidence in 2018.
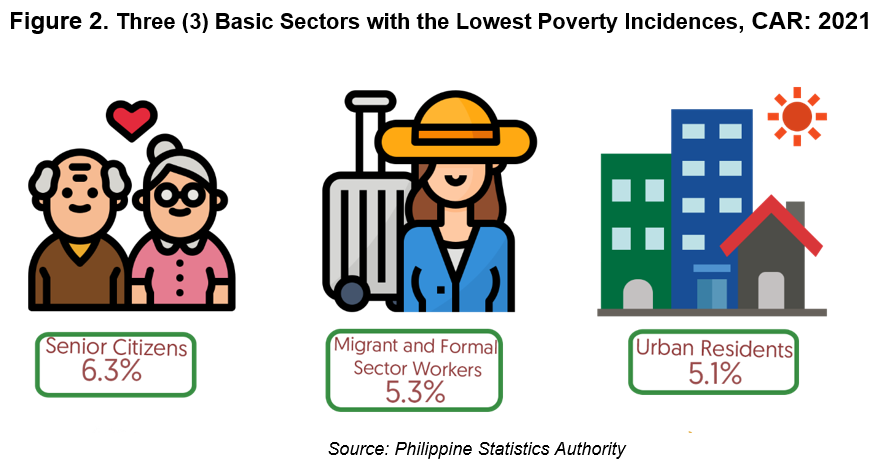
On the other hand, the sectors with the lowest poverty incidences in 2021 were senior citizens, migrant and formal sector workers, and urban residents with poverty incidences of 6.3 percent, 5.3 percent, and 5.1 percent, respectively.
These three sectors also registered the lowest poverty incidences in 2015 and 2018.
Two other sectors generated poverty estimates
In addition to the 9 basic sectors previously published, poverty estimates were also generated for other two sectors, namely: 1) individuals residing in rural areas and (2) self-employed and unpaid family workers. These are used as proxy indicators for workers in the informal sector.
All the sectors in the region exhibited significant reduction in poverty incidence, except for urban residence which showed an increase in poverty incidence from 4.9 percent in 2018 to 5.1 percent in 2021. There were no recorded sample household for fisherfolks.
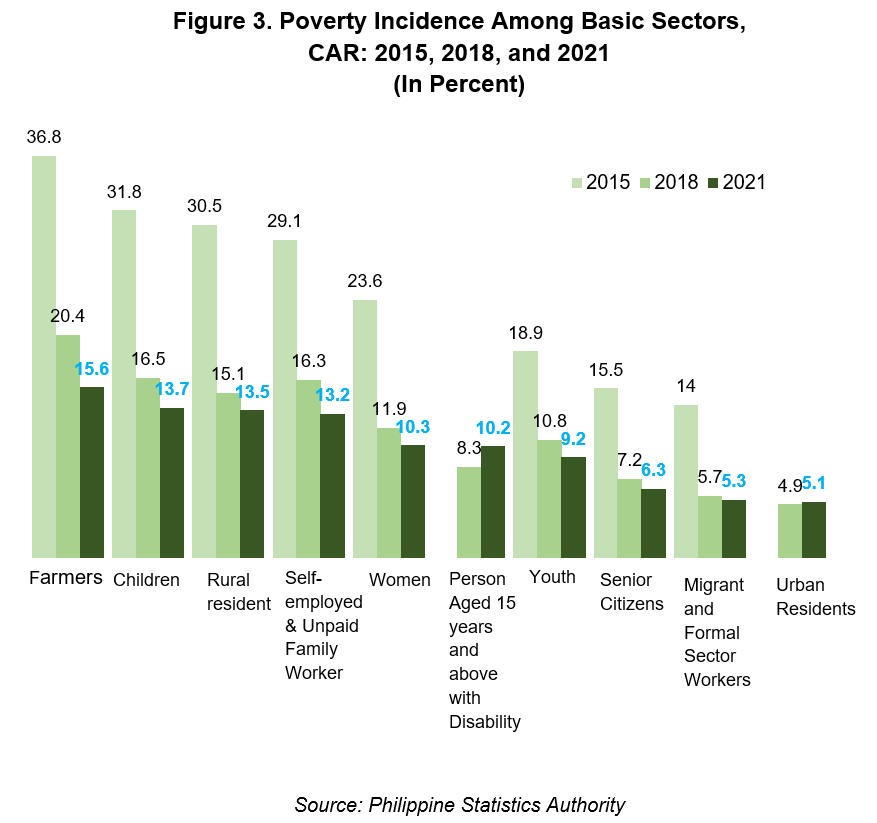
Rural residents have highest number of poor
Individuals residing in rural areas (belonging to poor families) were estimated to be 148 thousand, the highest among the basic sectors in the region in 2021. But the number was a reduction of 21.7 percent from the 2018 count of 189 thousand poor individuals, and reduction of 62.0 percent from the 2015 estimate of 389 thousand.
Women came second with an estimated 92 thousand poor individuals. In 2018, the number was 104 thousand poor women and in 2015 was 198 thousand poor women.
The third highest number of poor individuals in 2021 were children with an estimate of 89 thousand. Children refer to individuals below 18 years old based on, RA 7610, Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act. The number of poor children was estimated at 206 thousand in 2015 and 107 thousand in 2018.
ALDRIN FEDERICO R. BAHIT JR.
(Chief Statistical Specialist)
Officer-in-Charge
______________________________________________________
TECHNICAL NOTES
Poor refers to individuals and families whose income fall below the poverty threshold as defined by the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) and/or cannot afford in a sustained manner to provide their minimum basic needs of food, health, education, housing, and other essential amenities of life.
Poverty Threshold refers to the minimum income/expenditure required for a family/individual to meet the basic food and non-food requirements
Poverty Incidence refers to the proportion of families/individuals with per capita income/expenditure less than the per capita poverty threshold to the total number of families/individuals
Basic Sectors as defined in RA 8425 as the disadvantaged or marginalized sectors of the Philippine society, namely:
|
1. Farmer-peasant; 2. Artisanal fisherfolk; 3. Workers in the formal sector and migrant workers; 4. Workers in the informal sector; 5. Indigenous peoples and cultural communities; 6. Women; 7. Differently-abled persons; |
8. Senior citizens; 9. Victims of calamities and disasters; 10. Youth and students; 11. Children; 12. Urban poor; 13. Cooperatives; and 14. Non-government organization.
|
Child refers to individual below 18 years old based on, RA 7610, Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act.
Youth refers to individuals aged 15 to 30 years old, based on RA 8044, The Youth in Nation-Building Act.
Senior citizen refers to an individual aged 60 years old and above, based on RA 9257, the Expanded Senior Citizens Act
Migrant and formal sector workers refer to individuals who are Overseas Contract Workers (OCW) or Workers other than OCWs or employed persons working for private establishments and government organizations and corporations.
Farmers refer to employed individuals 15 years old and over whose primary occupation is farming, plant growing or animal production. These include occupations under Skilled Agricultural, Forestry and Fishery Works and Elementary
Self-employed and unpaid family workers refer to employed individuals 15 years old and over who are either self-employed or worked without pay on family-owned farm or business. This is a proxy indicator for the informal sector workers.
Functional difficulty is classified into six core difficulties. The concepts and definitions are based on the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) of the World Health Organization (WHO). These difficulties include the following: a) Difficulty seeing even if wearing eye glasses; b) Difficulty hearing even if using hearing aid; c) Difficulty walking or climbing steps; d) Difficulty remembering or concentrating; e) Difficulty with self-care; and f) Difficulty communicating.