
The 2020 Census of Population and Housing (2020 CPH) took a snapshot of the Philippine population as of May 1, 2020. Pursuant to Proclamation No. 1179, s. 2021 signed on July 6, President Duterte has declared official for all purposes the population counts by province, city/municipality, and barangay.
As of May 1, 2020, the Philippine total population was 109,035,343. The total population of the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) as of the same date was 1,797,660. This accounted for about 1.65 percent of the Philippine population in 2020.
The total population of senior citizens in the Philippines was 9,242,121.
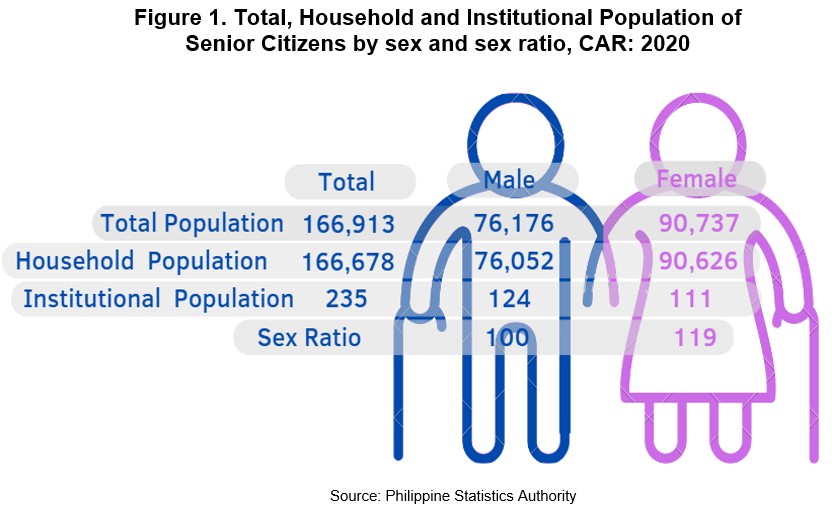
In CAR, the total population of senior citizens was 166,913. This was equivalent to 1.8 percent and 9.3 percent of the national total population of senior citizens and total population of CAR, respectively. It increased by 25.4 percent or 33,820 from the total population of senior citizens in 2015 with 133,093 count.
Population of senior citizens in households accounted for 99.9 percent or 166,678, and 0.1 percent or 235 persons in institutions.
Female senior citizens constituted 54.4 percent or 90,737 of the total population, while male senior citizens accounted for the rest of the 45.6 percent or a total of 76,176. The sex ratio was 119 female senior citizens in every 100 male senior citizens.
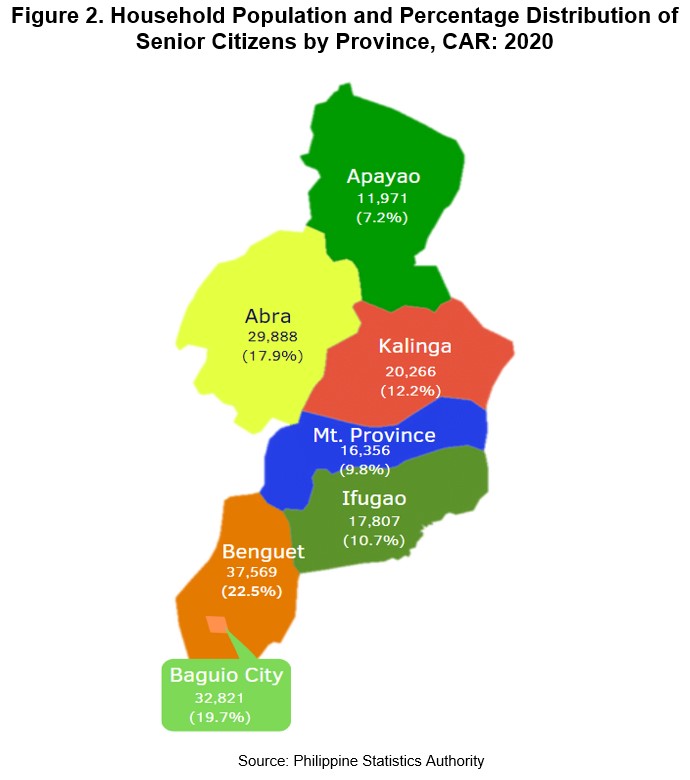
Among provinces and HUC, the highest number of population of senior citizens was recorded in the province of Benguet (excluding Baguio City), which accounted for 22.5 percent or 37,569 of the household population; followed by Baguio City with 19.7 percent or 32,821 persons; and Abra with 17.9 percent or 29,888 persons.
On the other hand, Apayao recorded the least number of senior citizens, accounting for only 7.2 percent or with a total of 11,971.
In all provinces, including Baguio City, female senior citizens outnumbered male senior citizens.
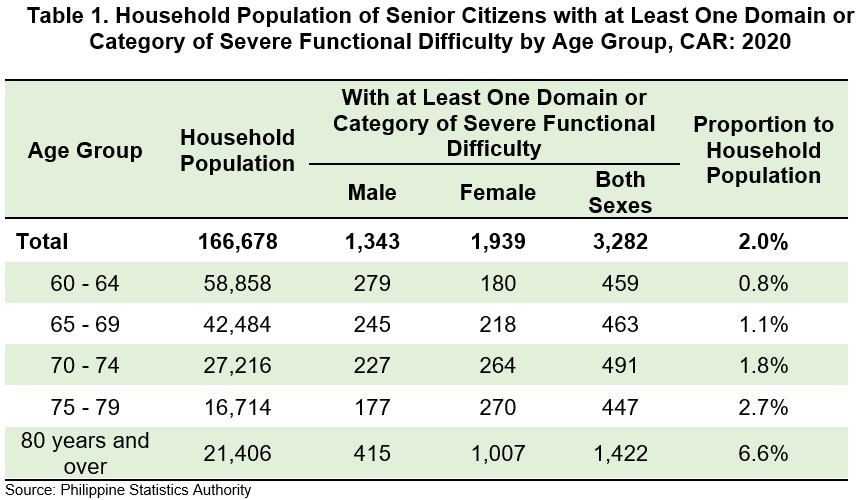
The number of senior citizens with at least one domain or category of severe functional difficulty was 3,282 or 2.0 percent of the household population. This meant that in every 100 senior citizens in CAR, 2 had severe difficulty (cannot do it at all) in either one or more of the following domain of functional difficulty: a) Difficulty in seeing, even when wearing glasses; b) Difficulty in hearing, even when using a hearing aid; c) Difficulty in walking or climbing steps; d) Difficulty in remembering or concentrating (cognitive); e) Difficulty with self-care such as washing all over or dressing; f) Difficulty in communicating using usual (customary) language.
Severe cases of functional difficulty were most prevalent among senior citizens aged 80 years and over accounting 43.3 percent or 1,422 of the total count of senior citizens with at least one domain or category of severe functional difficulty.
By sex, female senior citizens accounted for 59.1 percent or a total of 1,939 individuals, while male accounted for 40.9 percent or a total of 1,343 individuals. This meant that in every 10 senior citizens with at least one domain or category of severe functional difficulty, 6 were females.
VILLAFE P. ALIBUYOG
Regional Director
___________________________________________________________
TECHNICAL NOTES
Persons Included in the Census Enumeration - Included in the enumeration were those who were alive as of the census reference date, that is, 12:01 a.m. of May 1, 2020:
- Filipino nationals permanently residing in the Philippines;
- Filipino nationals who, as of May 1, 2020, were temporarily at Philippine sea, or were temporarily on vacation, business/pleasure trip or studying/training abroad and were expected to be back within a year from the date of departure;
- Filipino overseas workers, including those on board in oceangoing vessels, who were away as of May 1, 2020 but were expected to be back within five years;
- Philippine government officials, both military and civilian, including Philippine diplomatic personnel and their families, assigned abroad; and,
- Civilian citizens of foreign countries who have their usual residence in the Philippines, or foreign visitors who had stayed or are expected to stay for at least a year from the date of their arrival in this country.
Usual Place of Residence - All persons were enumerated in their usual place of residence which refers to the geographic place (street, barangay, city/municipality or province) where the person usually resides. As a rule, a person’s usual place of residence is the place where that person sleeps most of the time. Hence, it may be the same as or different from the place where he/she was found at the time of the census.
Household population comprises of persons who belong to a household. In determining the household membership, the basic criterion is the usual place of residence or the place where the person usually resides. This may be the same or different from the place where he/she is found at the time of the census. As a rule, it is the place where he/she usually sleeps.
Institutional population comprises of persons who are found living in Institutional Living Quarters (ILQs). They may have their own families or households elsewhere but at the time of the census, they are committed or confined in ILQ, wherein they are usually subject to a common authority or management, or bound by either a common public objective or a common personal interest.
Total population is the aggregate of the household and institutional population.
Senior citizen refers to any resident citizen of the Philippines at least sixty (60) years old (Republic Act 9994 – Expanded Senior Citizen’s Act of 2010).
Functional Difficulty were asked for household members five years and over. To identify household members who have functional difficulty, the respondents were asked, “Does ______ have difficulty…?”. It is instructed to read out each kind of functional difficulty one by one.
a. Seeing, even if wearing eyeglasses?
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have vision difficulties or problems seeing, even when wearing glasses (if they wear glasses).
Seeing refers to an individual using his/her eyes and visual capacity in order to perceive or observe what is happening around him/her.
b. Hearing, even if using a hearing aid?
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some hearing limitations or problems of any kind with their hearing, even when using a hearing aid (if they wear a hearing aid).
Hearing refers to an individual using his/her ears and auditory (or hearing) capacity in order to know what is being said to him/her or the sounds of activity, including the danger that is happening around him/her.
c. Walking or climbing steps?
The purpose of this question is to identify persons who have some limitations or problems of any kind getting around on foot.
Walking refers to the use of lower limbs (legs) in such a way as to propel oneself over the ground to get from point A to point B. The capacity to walk should be without assistance of any device (wheelchair, crutches, walker, and others) or human. If such assistance is needed, the person has difficulty walking.
d. Remembering or concentrating?
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some problems with remembering or focusing attention that contribute to difficulty in doing their daily activities.
Remembering refers to the use of memory to recall incidents or events. It means the individual can bring to mind or think again about something that has taken place in the past (either the recent past or further back). With younger people, remembering is often associated with storing facts learned in school and being able to retrieve them when needed.
Remembering should NOT be equated with memorizing or with good or bad memories.
Concentrating refers to the use of mental ability to accomplish some tasks, such as reading, calculating numbers or learning something. It is associated with focusing on the task at hand in order to complete the task.
e. Self-caring (such as washing all over or dressing)?
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some problems with taking care of themselves independently.
Washing all over refers to the process of cleaning one’s entire body (usually with soap and water) in the usual manner for the culture.
The washing activity includes cleaning hair and feet, as well as gathering any necessary items for bathing such as soap or shampoo, a wash cloth or water.
Dressing refers to all aspects of putting clothing or garments on the upper and lower body, including the feet if culturally appropriate.
f. Communicating using his/her usual (customary) language?
The purpose of this item is to identify persons who have some problems with talking, listening, or understanding speech such that it contributes to difficulty in making themselves understood to others or understanding others.
Communicating refers to a person exchanging information or ideas with other people through the use of language.
Communication difficulties can originate in numerous places in the exchange process. It may involve mechanical problems such as hearing impairment or speech impairment, or it may be related to the ability of the mind to interpret the sounds that the auditory system is gathering and to recognize the words that are being used or an inability of the mind to compose a sentence or say a word even when the person knows the word and sentence.
*******

