Human Settlements and Environmental Health is one of the six components of the United Nations Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES) 2013. This framework was adopted in the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) to come up with CAR Regional Compendium of Environment Statistics. Component 5 has two subcomponents namely, Human Settlements and Environmental Health.

Out of the five topics under this subcomponent, only two topics (i.e. access to selected basic services and environmental concerns specific to urban habitats) is presented. The data are gathered from the census of population and housing of PSA and the Department of Transportation (DOTr).
Access to water, sanitation and energy (Access to selected basic services)
Statistics regarding water and sanitation describe the access of the population to safe water sources and adequate sanitation facilities. The data for this subcomponent were taken from the 2010 Census of Population and Housing of PSA. It includes access to improved drinking water quality and improved sanitation facility.
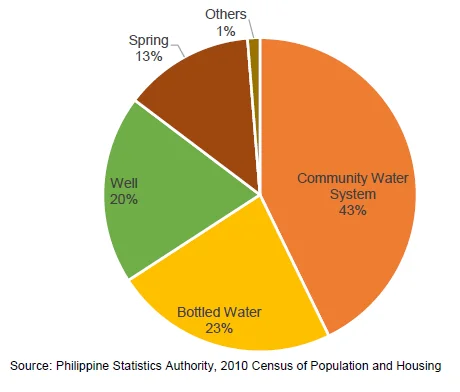
Most Cordillerans get their drinking water from community water system
- In 2010, 43 percent of the households in the region sourced their drinking water supply from community water system. Bottled water came second with 23 percent share. Households who get their drinking water from wells and springs comprised 20 percent and 13 percent of the total households, respectively.
Figure 1. Distribution of Households by Source of Drinking Water Supply,
CAR: 2010
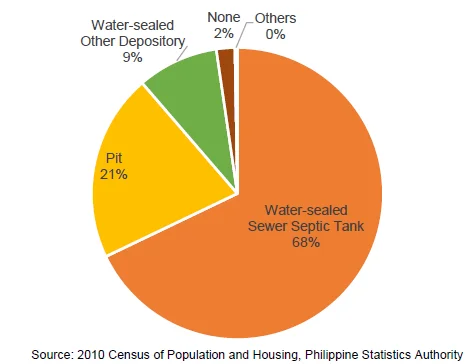
7 out of 10 households use water-sealed sewer septic tank as toilet facility
- Households with access to water-sealed sewer septic tank were 68 percent of the total 352,403 households in CAR. Out of the 21 percent of the total household who classified their toilet facility used as pit, 43 percent of them responded that they were still using open pit while 57 percent were using closed pit. Meanwhile, two percent or 7,203 households still had no access to any toilet facility in 2010.
Figure 2. Distribution of Households by Toilet Facility Used,
CAR: 2010
Environmental concerns specific to urban habitats
This topic has only one core statistics, that is, the number of private and public vehicles. The number of motor vehicles registered by type of registration for the years 2015 to 2018 was gathered as an indicator for this subcomponent. Data were gathered from the Department of Transportation - Land Transportation Office (DOTr – LTO). The DOTr-LTO reports seven types of motor vehicles including cars, utility vehicles (UV), sports utility vehicle (SUV), trucks, buses, trailers and motorcycles/tricycles.
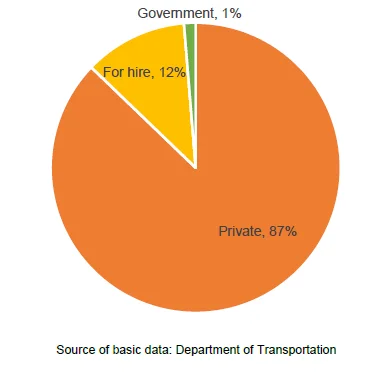
Registered vehicles in CAR are mostly private
- In 2018, a total of 169,235 vehicles were registered of which 90 percent where renewed and 10 percent were newly registered. Out of the total registered vehicles, 87 percent were private vehicles, 12 percent were vehicles that are for hire and only 1 percent were government vehicles.
Figure 3. Distribution of Registered Vehicles by Type
of Vehicle, CAR: 2018

The subcomponent has five topics wherein only water related diseases and conditions, and vector borne diseases have core statistics.
Water-related diseases and conditions
This topic includes all water related diseases and conditions that resulted from the ingestion of chemicals and micro-organisms. These include diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa, water-borne parasite infection and chemical contamination of water.
There are eight diseases and conditions presented under this topic. These pertain to the number of cases and deaths of diarrheas, acute respiratory tract infection and pneumonia, typhoid and paratyphoid fever, viral hepatitis, leprosy schistosomiasis, filariasis and leptospirosis. These data were gathered from the Department of Health (DOH) covering the period 2008-2018.
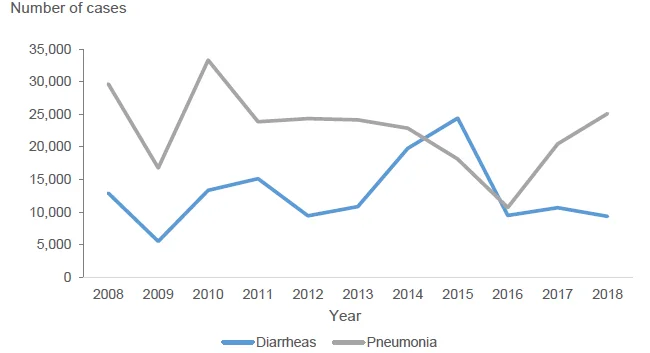
Diarrhea and pneumonia are the most recorded cases of water-borne diseases in CAR
- Diarrhea and pneumonia were the most prevalent water-borne diseases in the region. Pneumonia recorded the highest in 2010 with 33,305 cases, where 41.6 percent or 13,850 cases were diagnosed in the province of Benguet. The lowest recorded number of pneumonia was observed in 2016 with 10,715 cases.
- Meanwhile, diarrhea recorded the highest in 2015 with 24,412 number of cases of which majority of the recorded cases was seen in Baguio City with 7,460 persons affected. The least number of diarrhea cases was recorded in 2009 with 5,529 cases.
Figure 4. Number of Cases of Diarrhea and Pneumonia, CAR: 2008-2018
Vector borne diseases
The framework defined vector-borne diseases as those diseases that are transmitted by organisms such as insects and arachnids that carry viruses, bacteria, protozoa and other pathogens. Statistics on vector-borne diseases were gathered from the Department of Health (DOH). These include the number of cases and deaths for dengue and malaria.
Dengue cases rose to 2,767 in 2011
Figure 5. Number of Cases and Deaths from Dengue,
CAR:2008-2018
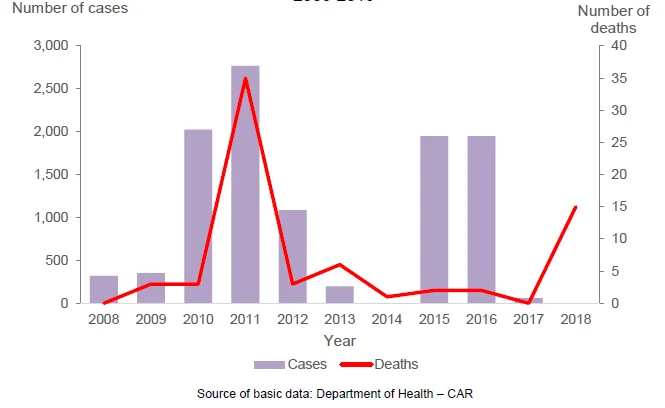
- Number of cases and deaths from dengue posted the highest in 2011 with 2,767 and 35, respectively. The total reported cases of dengue was 10,705 from 2008 to 2018. There were no cases recorded for the years 2014 and 2018. Malaria, on the other hand, posted the highest in 2008 with 150 cases and nine deaths.

