Environmental Conditions and Quality is one of the six components of the United Nations Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES) 2013. This framework was adopted in the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) to come up with CAR Regional Compendium of Environment Statistics. Component 1 has three subcomponents, one of which is the Land Cover, Ecosystem and Biodiversity.
Land Cover
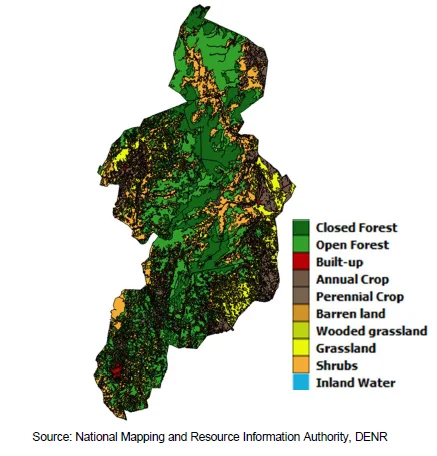
- The 2015 Land Cover map of CAR is the result of the latest national mapping activity carried out by NAMRIA.
Figure 1. CAR Land Cover: 2015
- It was generated by interpreting satellite images captured from Landsat 8 with 30-meter resolution and Google Earth.
- The land cover classification follows the DENR Department Memorandum Circular 2005-05: Adopting Forestry Definitions Concerning Forest Cover/Land Use and the Forest Resources Assessment (FRA) of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the UN. The classification is aggregated into 12 categories – Closed forest, Open forest, Annual crop, Perennial crop, Wooded grassland, Shrubs, Grassland, Built-up area, Fallow, Fishpond, Barren land, and Inland water.
Forestland covers 44.6% of the region
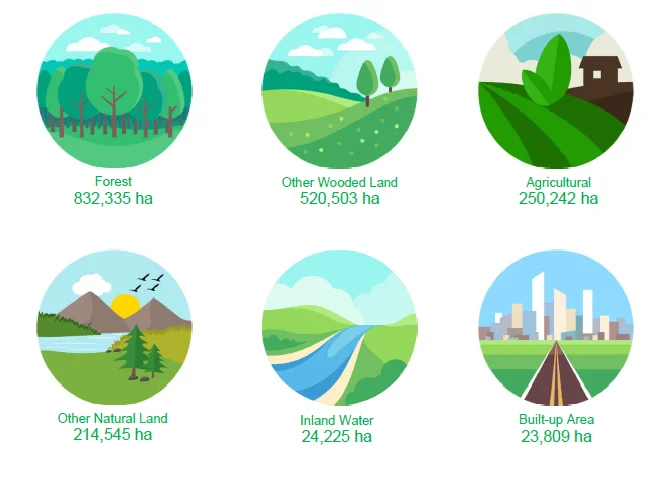
- The 12 categories were further divided into six groups, namely: (1) Forest, classified into Closed forest and Open forest; (2) Other Wooded Land, composed of wooded grassland, shrubs and fallow; (3) Agricultural, comprised of annual and perennial crop; (4) Other Natural Land, in which barren land and grassland belong to; (5) Inland water, that included fishpond and other inland waters; and (6) Built-up area.
- In 2015, the measure of land cover by group were the following:

Ecosystems and Biodiversity
- The region has a unique vegetation and is endowed with various varieties of flora and fauna. Biodiversity is a source of value in forest, first, that it participates directly in production such as wood, hunting, and forest amenities and in regulating production such as resilience in the face of hazards and uncertainties, and in adapting to changes. Many services rendered by the forest ecosystem often depend on biodiversity and thus reduce its value.
-
Second, its value lies in its non-market features such as culture, landscapes, philosophical and moral issues. But its value can be generally estimated by its replacement value which could run to hundreds of billions of pesos to restore the biodiversity of Cordillera region alone.
-
It could be sufficient to emphasize that human beings could not survive without the basic services provided by the natural ecosystems and the biodiversity that constitute them.
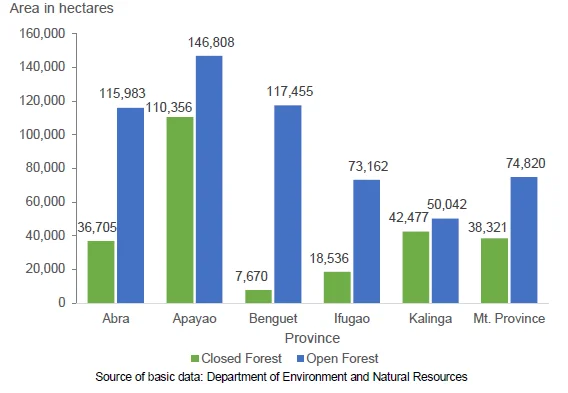
Apayao has the largest area of forest with 257 thousand hectares
- Forest cover in the region is further categorized into three types: Closed forest, where tree formations cover a high proportion exceeding 40 percent of the ground; Open forest where tree formations cover at least 10 percent and less than 40 percent; and Plantation forest where forest stands are established by planting or/and seeding.
- The area of natural forests is largest in the province of Apayao both in closed and open forests at 110,356 hectares and 146,808 hectares, respectively. Benguet had the smallest area of natural closed forest at 7,670 hectares while Kalinga had the smallest area of open forests at 50,042 hectares.
Figure 2. Area of Natural Forests by Province, CAR: 2015
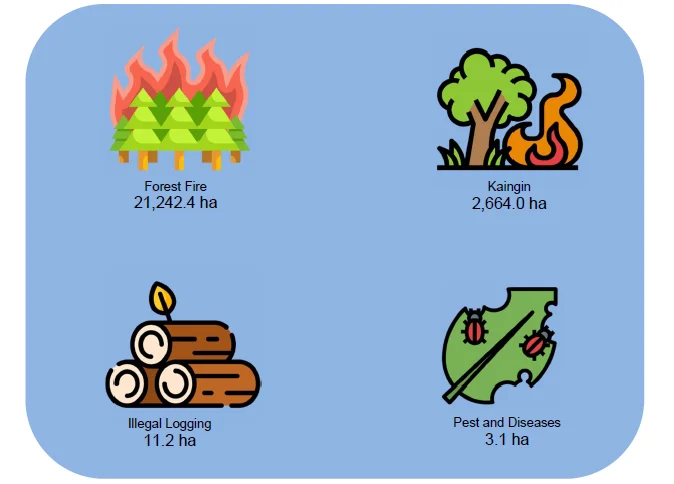
Forest disturbance affects 24 thousand ha from 2008 to 2018
- Forest disturbances peaked in 2010 affecting 8,527.8 hectares of which 96.4 percent or 8,216.6 hectares were affected by forest fires. The total forest disturbances during the period covered registered a total of 23,920.7 hectares.
Figure 3. Forest Disturbance, CAR: 2008 to 2018 (In hectares)
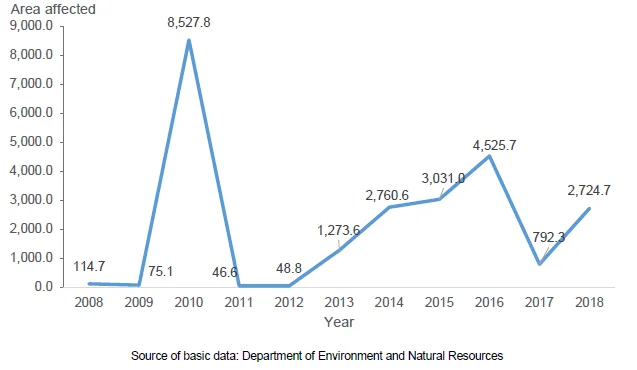
Figure 4. Area Affected by Forest Disturbances by Type: 2008-2018